Conquering the Silent Invader
Understanding Mould
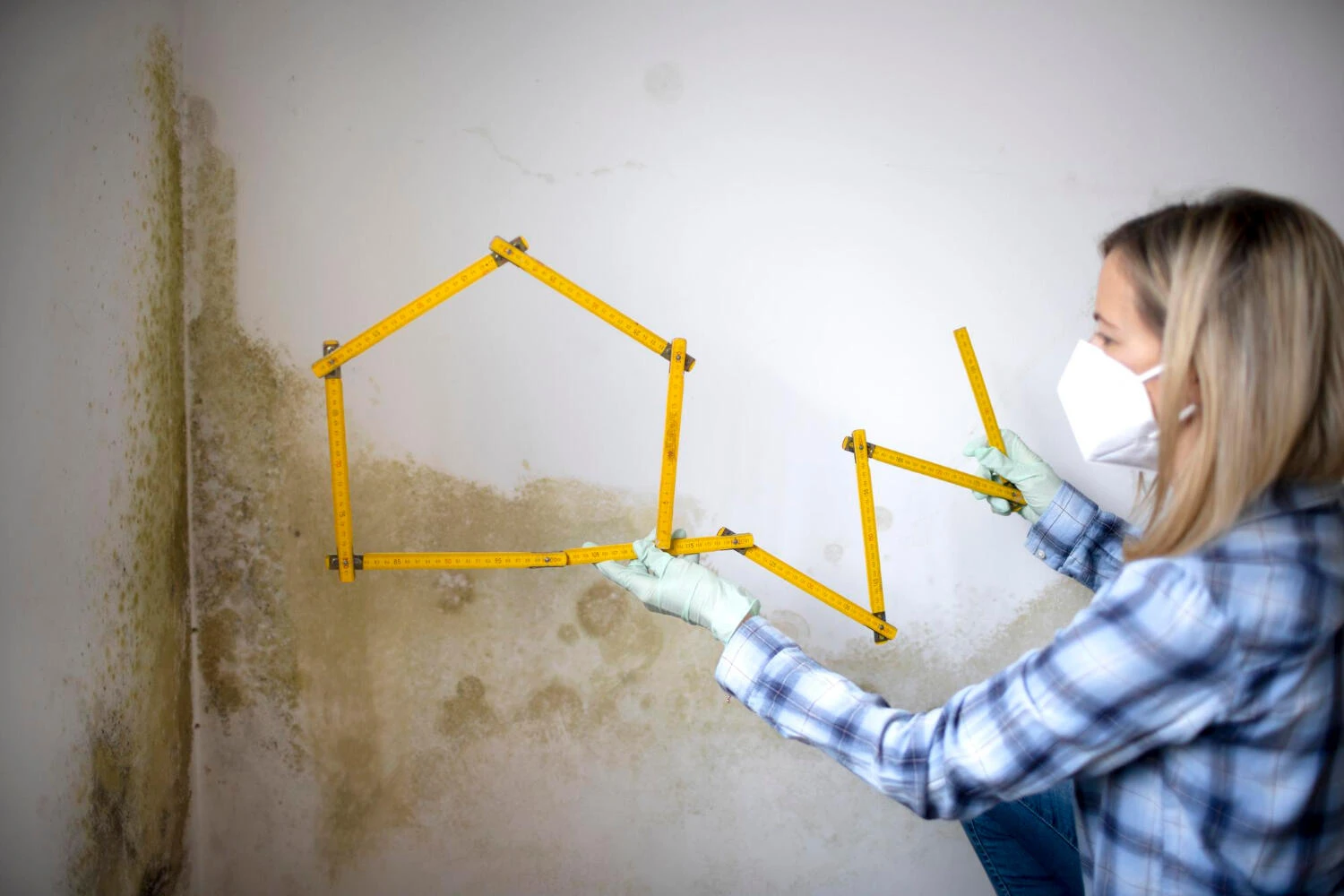
Mould is a type of fungus that thrives in damp, humid, and poorly ventilated environments. It reproduces through microscopic spores that can be found almost everywhere, indoors and outdoors. The key to mould management is understanding its life cycle and how it infiltrates your home.

Recognising the Signs
- Visible Mould: This can appear as fuzzy spots, black streaks, or discoloured patches on walls, ceilings, or other surfaces.
- Musty Odour: A strong, musty smell is a telltale sign of mould growth.
- Allergic Reactions: Persistent sneezing, coughing, itchy eyes, or skin rashes can be a result of mould exposure.
Prevention
- Control Moisture: Mould thrives on moisture, so fix leaks promptly and ensure proper ventilation in bathrooms, kitchens, and basements.
- Monitor Humidity: Maintain indoor humidity levels below 60%, ideally between 30% and 50%. Use dehumidifiers if necessary.
- Proper Insulation: Insulate your home to prevent condensation on cold surfaces, such as windows or pipes.
- Regular Cleaning: Routinely clean and maintain your home, especially in areas prone to moisture, like bathrooms and kitchens.
- Landscaping: Ensure proper drainage away from your home’s foundation to prevent water from seeping into basements or crawl spaces.
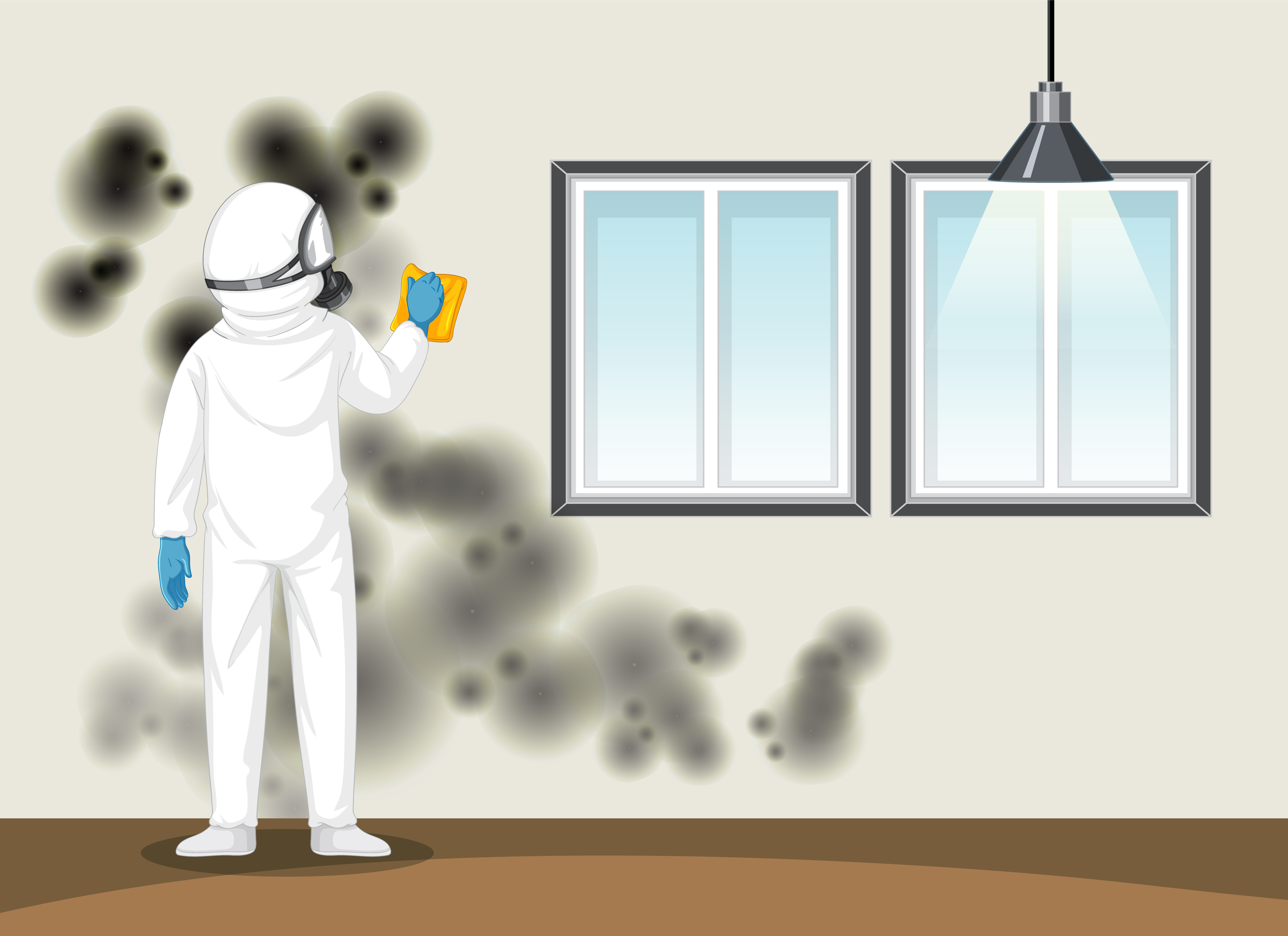
Mould Removal
- Safety First: Before tackling mould, protect yourself with gloves, a mask, and eye protection. Open windows for ventilation.
- Identify the Affected Areas: Determine the extent of the mould infestation and identify all affected surfaces.
- Containment: Isolate the affected area using plastic sheeting and tape to prevent the spread of spores.
- Removal: Scrub the mouldy surface with a mixture of water and detergent. For stubborn cases, use a solution of one cup of bleach per gallon of water. Ensure proper ventilation during this process.
- Dispose: Safely dispose of mould-infested materials in sealed bags.
- Prevent Future Growth: After removal, address the root cause of the mould issue, such as fixing leaks or improving ventilation.
Hiring Professionals
- Experience: Choose a contractor or specialist experienced in mould remediation.
- References: Ask for references and reviews from previous clients.
- Licensing and Insurance: Ensure the professional is licensed and carries liability insurance.
- Estimates: Obtain estimates from multiple professionals to compare pricing and services.
Health Concerns
- Mould: Can cause a range of health issues, especially in individuals with allergies or respiratory conditions. If you or your family members experience persistent health problems, consult a healthcare professional.
Post-Removal Cleaning
- After Mould Removal: Clean and disinfect the area to prevent future mould growth.
- Consider Mould-Resistant Materials: Use mould-resistant paint or materials in moisture-prone areas.
Routine Maintenance
- Once Your Home is Mould-Free: Implement a routine maintenance plan to prevent future infestations.
- Regular Inspections: Regularly inspect areas where mould is likely to occur and address any issues promptly.

Conclusion
Mould management is a crucial aspect of homeownership that should not be ignored. By understanding mould’s behaviour, recognising its signs, and implementing preventive measures, you can protect your home and family from the harmful effects of mould. If mould does infiltrate your home, tackle it promptly, and consider seeking professional assistance when needed. With diligence and a proactive approach, you can conquer the silent invader and enjoy a healthier, mould-free living environment.